.
As the world moves towards sustainable energy solutions, India is exploring alternative fuels to meet its growing transportation demands while addressing environmental concerns. One promising solution gaining attention is hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). These vehicles use hydrogen to generate electricity, producing only water as a by-product, making them a zero-emission alternative. While electric vehicles (EVs) have dominated the conversation in India, hydrogen FCVs present unique opportunities for the country’s long-term sustainability goals.
What Are Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles ?
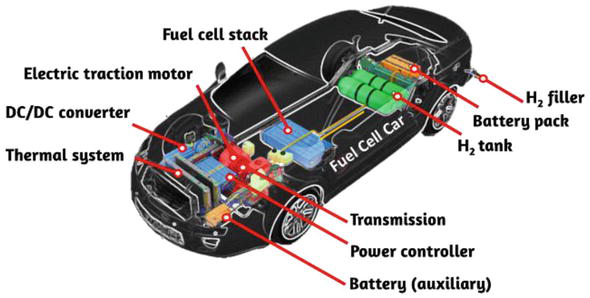
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles generate electricity by converting hydrogen gas into electrical energy through a chemical process. Unlike battery-electric vehicles (BEVs), which store electricity in batteries, FCVs generate electricity on the go, allowing for longer driving ranges and quicker refueling times. This makes them particularly suitable for long-haul transportation, commercial vehicles, and areas where charging infrastructure is underdeveloped.
Advantages of Hydrogen FCVs for India
1. Zero Emissions: Hydrogen FCVs emit only water vapor, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional fossil fuel vehicles. This could help India significantly reduce its carbon footprint, particularly in urban areas suffering from air pollution.
2. Energy Independence: Hydrogen can be produced domestically using renewable energy sources like solar and wind, reducing India’s dependence on imported oil and fossil fuels.
3. Scalability: Unlike electric vehicles, which require a vast charging network, hydrogen FCVs can be refueled in minutes, similar to conventional vehicles. This scalability makes them a viable option for commercial fleets and public transportation.
Challenges Hindering Adoption
1. High Costs: One of the primary challenges for hydrogen FCVs in India is the high cost of production and infrastructure development. Currently, hydrogen fuel cells are expensive to produce, and setting up hydrogen refueling stations requires significant investment.
2. Infrastructure: India’s hydrogen infrastructure is still in its infancy. A robust network of hydrogen production, storage, and distribution facilities is crucial for the widespread adoption of FCVs.
3. Technological Hurdles: Hydrogen storage and transportation pose safety risks that need to be addressed through technological advancements. Ensuring safe and efficient delivery systems is essential for building consumer confidence.
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
The Indian government is taking steps to promote hydrogen as a clean fuel under its National Hydrogen Mission, launched in 2021. The mission aims to make India a global hub for hydrogen production and export, with a focus on green hydrogen generated from renewable energy. Several pilot projects, including hydrogen-powered buses and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), are being tested in cities like Delhi and Bangalore. These efforts are laying the groundwork for broader adoption of hydrogen technology in the future.
Potential Applications in India
1.Public Transportation:Hydrogen-powered buses and trains are an ideal solution for India’s vast public transportation system, offering a clean and efficient alternative to diesel-powered vehicles.
2. Commercial Vehicles: Long-haul trucks and commercial fleets can benefit from hydrogen’s longer range and quicker refueling times, making them more practical than battery-electric alternatives for these sectors.
3. Industrial and Heavy Machinery: Hydrogen fuel cells can be used in industrial equipment, mining machinery, and other heavy-duty applications where electric batteries may not provide sufficient power or range.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles hold significant promise for India’s future mobility landscape. While challenges such as high costs and infrastructure limitations exist, ongoing government support, technological advancements, and investments in hydrogen production can help overcome these barriers. As India pushes toward cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions, hydrogen FCVs could play a crucial role in decarbonizing the transportation sector, offering a viable alternative to electric vehicles and fossil fuels.
The future of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in India is still evolving, but with the right policies and investments, they could become a key player in the country’s transition to green energy.